Strengthening the Foundational Role of Consumption
Consumption is the foundation of economic development. Currently, insufficient domestic demand, particularly sluggish consumption, has emerged as a prominent challenge in the operation of China’s economy. Moreover, the external environment has become increasingly complex and severe. In response to these challenges, both the Central Economic Work Conference last year and this year’s Report on the Work of the Government have underscored the imperative of vigorously boosting consumption and investment returns and stimulating domestic demand. Boosting consumption has now become the top priority in advancing China’s current economic initiatives.
I. Fully understanding the foundational role of consumption in economic development
In recent years, amid a complex landscape characterized by intensifying external headwinds and mounting domestic challenges, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China (CPC) with Xi Jinping at its core has resolutely implemented a strategy to expand domestic demand, continuously reinforcing the underpinning role of domestic demand in driving economic development. The foundational importance of consumption has been steadily strengthened. Traditional consumption sectors, such as food, clothing, housing, and transportation, have seen significant growth, while emerging consumption areas, including digital services and electronics, have undergone rapid expansion. As a result, China has maintained its position as the world’s second-largest consumer goods market and the largest online retail market for over a decade.
Consumption serves as both the driving force and the outcome of economic development. Living a better life is the most fundamental aspiration of the people and the overarching objective of China’s development. The pursuit of a fulfilling livelihood is the primal impetus for human participation in economic activities. Only by increasing consumption and expanding market demand can production be driven upward, thereby enlarging the aggregate distributable economic pie and increasing the income of urban and rural residents. This will further expand consumption and promote the continued growth in production. As a result, a self-reinforcing cycle will be formed where consumption propels production, which in turn meets consumption demands and drives sustained economic growth.
Since the launch of reform and opening up in 1978, China’s economic development has been accompanied with continuous upgrading of consumption. In the early stages of reform and opening up, China significantly increased the procurement prices for agricultural products and raised the wages of urban industrial workers. These measures helped to achieve a more coordinated and balanced proportion of agriculture and industry, light and heavy industries, accumulation and consumption, etc., in the national economy. As a result, the consumer goods market continued to expand, creating vast opportunities for the rapid growth of light industry.
Wave upon wave of consumption upgrading among urban and rural residents, along with rising tides of the manufacturing sector, have propelled China’s rapid emergence as an industrial nation. During the 1980s, the so-called “old triad” of bicycles, sewing machines, and watches dominated household acquisitions. The 1990s witnessed a shift toward the “new triad” comprised of color televisions, refrigerators, and washing machines. Entering the 21st century, mobile phones, computers, and automobiles have emerged as principal consumption indicators. Consumer spending has sustained prolonged double-digit growth, driving the rapid expansion of related industries and fostering sustained economic development. This dynamic has provided critical support for achieving two globally unprecedented milestones: rapid economic advancement and enduring social stability.
In the current context, among the three drivers of economic growth, namely consumption, investment, and exports, the role and significance of consumption have become increasingly prominent. The expansion of investment is now confronting a critical bottleneck as traditional infrastructure investment in sectors such as railways and highways enters a post-peak phase, whereas investment in next-generation infrastructure encompassing big data, artificial intelligence (AI), and renewable energy remains inadequate in compensating for the resultant shortfall. In particular, the manufacturing sector is undergoing a pivotal structural transition, and investment is shifting from focusing on expanding scale to a greater emphasis on improving efficiency and effectiveness. At the same time, as external demand is encountering pronounced challenges, China’s transition toward diminishing reliance on export-driven growth has become an inevitable trend. In this context, consumption has emerged as the primary driver of economic growth and a critical stabilizer for ensuring overall stable performance of economy, serving as the key to expanding domestic demand across all dimensions.
However, over the past several years, consumption as the principal driver of economic growth has exhibited pronounced volatility. Sluggish consumption has emerged as a critical constraint, with growth rates decelerating from double-digit to single-digit level. In 2024, driven by the consumer goods trade-in programs, total retail sales of consumer goods registered a year-on-year increase of 3.5%. Nevertheless, the consumption growth rate remains markedly lower than the economic growth rate, indicating that the foundational role of consumption in driving economic development has yet to fully demonstrate itself. In 2024, China’s final consumption expenditure contributed 44.5% to economic growth, driving GDP expansion by 2.2 percentage points; gross capital formation accounted for 25.2% of growth contribution, propelling GDP growth by 1.3 percentage points; net exports of goods and services generated a 30.3% contribution share, advancing GDP growth by 1.5 percentage points. Due to escalating external uncertainties, the contribution of foreign trade to economic growth lacks long-term sustainability. Since 2008, only a limited number of years have seen net exports of goods and services contributing more than one percentage point to GDP growth.
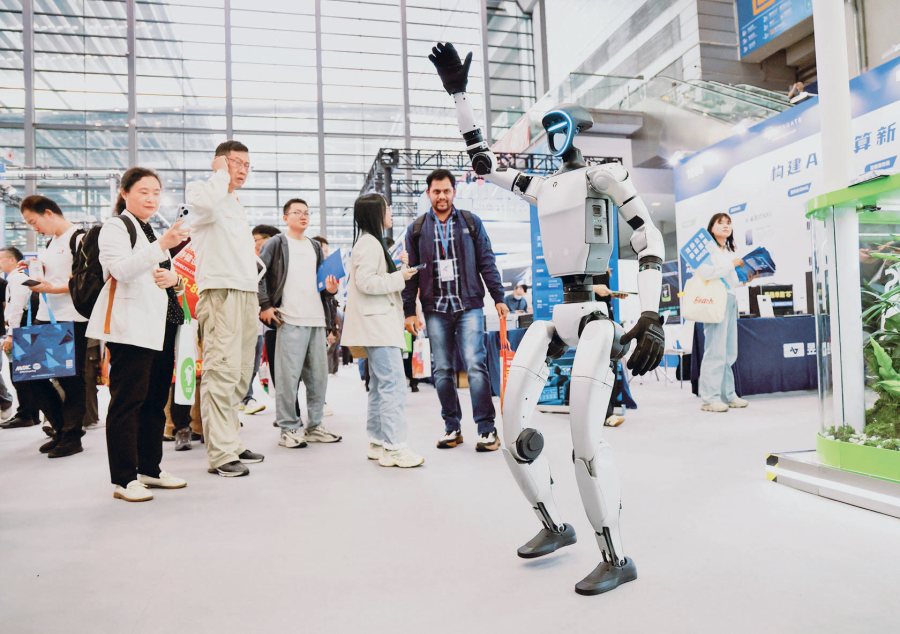

Visitors watch a demonstration of a humanoid robot on the opening day of the 13th China Information Technology Expo (CITE 2025) in Shenzhen Convention & Exhibition Center (Futian), Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, April 9, 2025. Over 1,000 enterprises participated in the event. PHOTO BY XINHUA REPORTER LIANG XU
This year, the external environment is becoming increasingly complex and severe, potentially exerting greater pressure on China’s foreign trade and other relevant sectors. Given this, it is imperative to enhance our sense of urgency in vigorously boosting consumption, swiftly address consumption deficiencies, and offset the insufficiencies in investment and export demand. By doing so, we will be able to promote sustained economic recovery and growth.
II. Accurately identifying the potential and key areas to boost consumption
Boosting consumption is not only an inherent requirement to meet the people's aspiration for a better life, but also a practical necessity for promoting economic recovery and growth. China's economy boasts a solid foundation, multiple strengths, great resilience, and vast potential. The supporting conditions and underlying trend for long-term economic growth have not changed. China's industrial foundation remains solid, while the new growth drivers play an increasingly important role in fueling economic growth. Through comprehensive reform and opening up, our development vitality and momentum will be further unleashed, and diversified and stable economic and trade relations will continue to expand. The macroeconomic regulation system and policies will be further improved. All this will provide a full guarantee for maintaining a steady and healthy economic development.
China's economy has been transitioning from a stage of rapid growth to one of high-quality development. In this new stage, both the requirements and conditions for development have exhibited new features. Notably, the people's aspiration for a better life has evolved from a focus on sufficiency to quality. Under the new circumstances, the critical focus of economic development has shifted toward fulfilling people's diverse, multileveled, and multifaceted demands by enhancing the provision of high-quality products and services and facilitating sound dynamics between supply and demand.
Overall, we should precisely identify and leverage the following five advantages in the current phase while implementing policies aimed at boosting consumption.
First, a continuous and robust capacity for consumption
Consumption is positively correlated with income. In recent years, as the national economy has sustained a recovery and growth, the incomes of both urban and rural residents in China have increased steadily. Specifically, the per capita disposable income of urban residents increased from 39,251 yuan in 2018 to 54,188 yuan in 2024, while that of rural residents rose from 14,617 yuan to 23,119 yuan during the same period. Between the 1980s and 2024, China's national savings rate has consistently ranged from 36% to 45%. In 2024, the national savings rate reached 43.4%, and the total balance of household deposits increased to 151.25 trillion yuan, with the per capita deposit surpassing 100,000 yuan for the first time.
Overall, both urban and rural residents in China have the financial capability for consumption and demonstrate a clear demand for consumption upgrading. The view that attributes sluggish consumption to insufficient purchasing power is overly simplistic and overlooks the objective reality of the sustained growth in residents, savings.
Second, vast potential for increasing consumption
Currently, the gap in consumption levels between urban and rural residents, as well as among various groups in China, remains relatively significant. For example, in 2024 the per capita consumer spending among urban residents amounted to 34,557 yuan, whereas that of rural residents totaled 19,280 yuan, resulting in a disparity of 15,277 yuan between the two groups. Should this gap be reduced by half in the future, the aggregate consumption expenditure of rural residents would increase by at least 3.5 trillion yuan.
Moreover, China’s overall consumption remains insufficient and lags significantly behind that of developed countries. Currently, the per capita consumer spending in the United States is roughly eight times that of China. Although its total population is only around 23.7% of China’s, the US consumer market is nearly 2.7 times larger. This highlights the vast potential for expanding consumption in China by narrowing the gap with developed economies, such as Europe and the United States, and raising the national consumption rates.
Third, an enormous demand for consumption upgrading
China has more than 1.4 billion people, making it one of the largest consumer markets in the world. At present, as major changes are taking place in the structure of urban and rural consumer spending, upgrading consumption through alignment with modern technologies and production modes can unleash immense potential in domestic demand. In particular, China boasts the world’s largest and most dynamic middle-income group of over 400 million people, holding the potential to generate substantial demand for consumption upgrading and to create new growth areas and development opportunities for the consumer market.
In recent years, China’s cultural and tourism consumption has been robust, while information consumption continues to gain momentum. Green products represented by new-energy vehicles have emerged as a new hot spot of consumer spending. According to the statistics of the China Automobile Dealers Association, retail sales of new-energy vehicles totaled about 10. 9 million in 2024, an increase of 40.7 percent, and the retail market penetration rate reached 47.6 percent.
Fourth, sufficient room for policy adjustments
Adjustments to consumption policies are crucial to unleashing the potential of consumer spending. Since last year, China has intensified efforts to promote large-scale equipment upgrades and consumer goods trade-in programs, achieving remarkable results in expanding effective demand. In 2024, the central government issued 150 billion yuan of ultra-long special treasury bonds to support local governments in implementing consumer goods trade-in programs, driving the total sales of automobiles, home appliances, home furnishings, and electric bicycles to exceed 1.3 trillion yuan. Notably, automobile trade-ins alone surpassed 6.8 million units, generating 920 billion yuan of sales. With the introduction of policies on large-scale equipment upgrades and consumer goods trade-in programs, investment in equipment purchases increased by 15.7 percent and retail sales of home appliances increased by 12.3 percent.
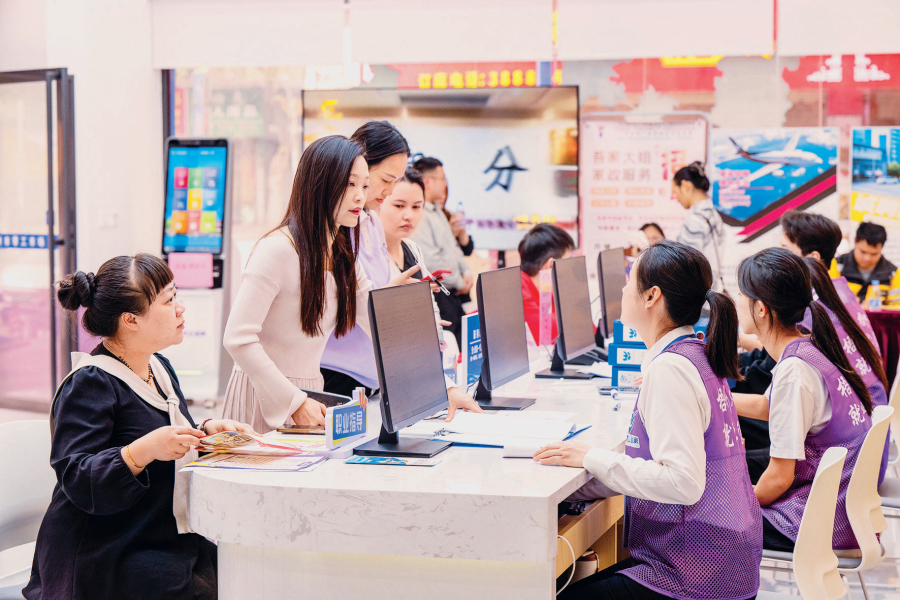

Job seekers consult with staff at a temporary employment market, Wanxiu District, Wuzhou City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, April 8, 2025. Combining online and offline approaches, temporary employment markets serve casual, temporary, and short-term workers as well as other employment groups, effectively promoting flexible employment through multiple channels. PEOPLE'S DAILY / PHOTO BY HE HUAWEN
This year, these policies will be implemented with greater intensity and extended to more sectors. We will expand the coverage of incentives for vehicle scrapping and renewal and provide subsidies for purchasing new digital products such as mobile phones, tablets, and smart watches (smart bracelets). In addition, as people’s living standards continue to improve, the consumption structure has undergone comprehensive upgrading, and the composition of demand has rapidly changed. There also remains significant room for adjustments to relevant tax policies.
Fifth, significant potential for expanding consumption
The advance of technologies such as the internet, big data, and AI has helped foster new forms and modes of consumer spending. New consumption forms such as product live streaming and social networking e-commerce have emerged one after another. Digital culture and tourism, online fitness, and other new consumption modes are flourishing. New scenarios like smart homes and smart wearable devices expand constantly. All of this has provided more choices for consumers and convenient consumption patterns and will continue to spur new consumption potential. For instance, the film Nezha 2, which was released this year, grossed a total box office of more than 15 billion yuan, which demonstrates China’s vast cultural creativity and market consumption potential.
III. Focusing on key priorities in boosting consumption
Consumption is an important engine driving China’s economic growth. To better leverage the foundational role of consumption in stimulating economic growth, it is essential to embrace the trend of consumption upgrading. We should enhance and expand conventional consumption while developing emerging consumption, boost service consumption, increase public spending as necessary, and work to satisfy personalized, diverse, and high-quality consumer demands.
Promoting personal income growth through various avenues
We will implement plans to support employment in key areas and sectors, urban and rural communities, and micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs). We will step up employment support in response to new developments and promote reasonable increases in salary-based incomes of key groups.
We will take multiple measures to stabilize the stock market, develop more bond products suitable for individual investors, and expand the channels for people to increase property income.
To increase rural incomes, we will intensify work-relief policies in key projects and the construction of small and medium-sized agricultural and rural infrastructure, improve the mechanisms for ensuring the incomes of grain growers and distributing returns gained from the appreciation of land. We will explore ways to put to good use rural residents’ legally owned houses by leasing them out, contributing them in the form of shares, or engaging in cooperative ventures.
Policies will be implemented to appropriately raise basic pension benefits for retirees, basic old-age benefits for rural and non-working urban residents, and government subsidies for basic medical insurance for rural and non-working urban residents. We will strengthen support for childcare and parenting and look into establishing a system of childcare subsidies. Localities where conditions permit will be encouraged to provide assistance funds or more one-off living allowances for people in difficulty as appropriate.
Fully implementing consumer goods trade-in programs
This year, ultra-long special treasury bonds totaling 300 billion yuan will be issued to support local governments in implementing consumer goods trade-in programs. It is crucial to make good use of these funds to promote green and intelligent upgrading of durable big-ticket items such as automobiles, home appliances, and home furnishings, as well as to support the replacement of old electric bicycles with certified and safer ones. We will optimize fund allocation for consumer goods trade-in programs, with priority given to durable big-ticket items. The subsidy standards for vehicle replacement and renewal will be refined. We will simplify application and payment procedures for subsidies, improve oversight mechanisms for relevant funds, and strengthen price monitoring on consumer goods included in our subsidy schemes. Additionally, we will crack down hard on price fraud and on fraud and misappropriation of subsidies that violate regulations.
Vigorously developing service consumption
We will boost consumption of services and increase the diversified supply of eldercare and childcare as well as health, disability, and domestic services by expanding access, reducing restrictions, and improving supervision in these sectors. We will improve the supply of services for eldercare and childcare, actively develop the anti-aging industry and silver tourism, and unleash the potential of the silver consumption market.
To expand consumption in culture, sports, and tourism, we will support tourist attractions, museums, and other cultural institutions in developing more service programs, appropriately extending business hours, and improving their capacity to receive visitors. We will streamline the approval procedures for commercial performances and sports events and introduce a system under which a single approval is valid for nationwide tours.
Trials for opening up in telecommunications, medical services, education, and other sectors will be expanded. With a focus on the demand for consumption upgrading, we will promote imports of quality consumer services such as healthcare, culture, and entertainment.
Fostering new types of consumption
We will create a full range of new consumption scenarios to accelerate the growth of digital, green, smart, and other emerging consumption. Under the initiative to upgrade digital consumption, we will promote AI plus consumption models, accelerate the development and application of new technologies and products, such as autonomous driving, smart wearable devices, ultra-high definition video, brain-computer interface, robotics, and additive manufacturing, and open up new arenas for high-growth consumption. We will move faster to improve oversight systems for the low-altitude economy and develop low-altitude consumption such as low-altitude tourism, aviation sports, and consumer drones in an orderly manner. We will improve management mechanisms and industry standards for new types of consumption such as yachting and recreational vehicle camping and continuously work to develop more cruise lines and tourism products.
Further refining policies on consumption
We will overhaul unreasonable restrictions on consumption in a timely manner and promote a shift from regulating the purchase of consumer goods such as automobiles to regulating their use. We will ensure effective implementation of the paid annual leave system and encourage employees to combine their paid leave with public holidays for flexible, staggered vacations. Places where conditions permit will be encouraged to explore the arrangement of spring and autumn vacations for middle and primary school students. We will make continued efforts to stem the downturn and restore stability in the real estate market and implement tax policies that are conducive to the stable and sound development of the real estate market, so as to better meet the demand for housing consumption. We will refine policies on the entry and residence of foreign nationals and on duty-free stores and facilitate inbound consumption. We will employ policy instruments, such as government subsidies and loan interest subsidies, and leverage the role of fiscal policies in driving consumption. Financial institutions are encouraged to increase loans to individual consumers while controlling risks and appropriately set the quota, term, and interest rate of these loans.
Working to improve the consumption environment
We will better coordinate fiscal, tax, financial, industrial, and investment policies with consumption policies, and increase effective investment in consumption infrastructure, improvement of consumption services, and new forms and modes of consumer spending. We will support eligible projects in sectors such as consumption, culture, and tourism in issuing real estate investment trusts (REITs) for developing infrastructure. Greater support will be provided for nighttime consumption hubs in terms of business venues, public transport capacity, and temporary parking spaces. We will continue with our efforts to build a number of cities into international centers of consumption and tap into their consumption potential. We will fully implement the three-year initiative for improving the consumption environment, regulate business practices in online sales, especially product live streaming, and provide stronger protection for consumer rights and interests, thereby creating a safe and reassuring consumption environment.
Yin Yanlin is Deputy Director of the Committee on Economic Affairs of the National Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference.
(Originally appeared in Qiushi Journal, Chinese edition, No. 9, 2025)