Good start to Chinese economy boosts confidence in global economic recovery
* Data from the National Bureau of Statistics showed Tuesday that China's gross domestic product (GDP) grew 4.5 percent year on year in the first quarter, beating the consensus forecast and marking the highest growth in a year.
* The International Monetary Fund (IMF) last week projected a 5.2 percent growth for China in 2023, up from 3 percent last year. The World Bank, meanwhile, expects China's GDP growth to rebound to 5.1 percent in 2023. Both are in line with China's official growth target of around 5 percent.
* With its vast economic volume and deep integration into the global economy, China's stronger-than-expected rebound is widely expected to promote growth in the Asian region and beyond, boosting confidence in global economic recovery.
BEIJING -- Newly released data indicated that the Chinese economy is recovering with stronger-than-expected momentum, kicking off the year with a good start and boosting confidence in a tepid global economic recovery.
Data from the National Bureau of Statistics showed Tuesday that China's gross domestic product (GDP) grew 4.5 percent year on year in the first quarter, beating the consensus forecast and marking the highest growth in a year.
China's robust rebound -- according to economists and observers -- is crucial to a sluggish global economic recovery amid still-elevated inflation and higher interest rates, as roughly 90 percent of advanced economies are projected to see a decline in their growth rate this year.
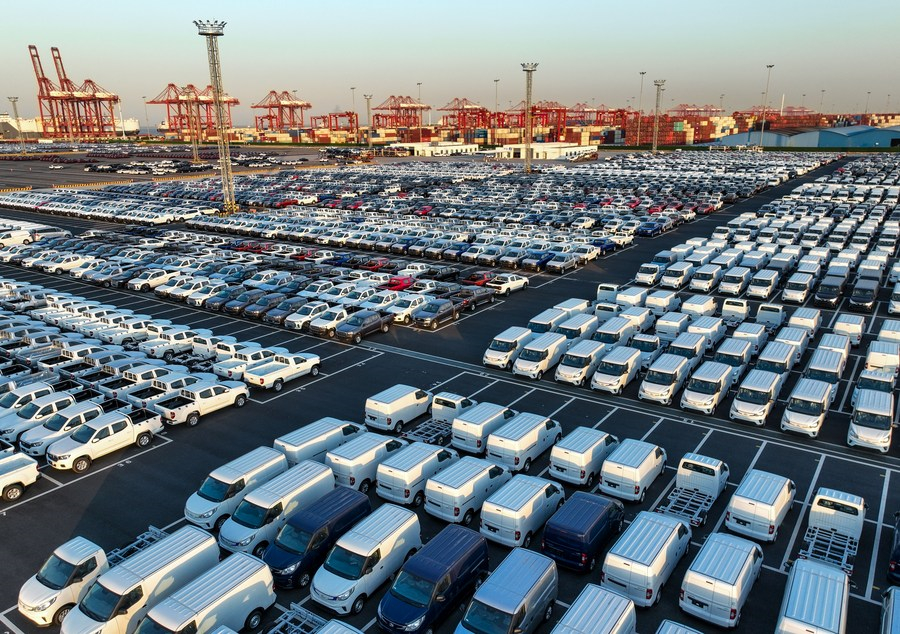

This aerial photo taken on March 13, 2023 shows vehicles at a terminal of Taicang Port, east China's Jiangsu Province. [Xinhua/Li Bo]
FASTER-THAN-EXPECTED GROWTH
The 4.5-percent growth in the first quarter, much faster than the 2.9-percent increase in the fourth quarter of last year, came as the country secured a smooth transition in its COVID-19 prevention and control measures.
"Efforts to propel China out of its pandemic-induced lethargy are paying off, as the lifting of lockdown restrictions and big stimulus packages propel growth higher than expected," said Susannah Streeter, head of money and markets at Hargreaves Lansdown, a British financial service company.
"As consumer confidence has grown and production has got back on track, retail sales have jumped to a two-year high and industrial output has picked up a pace not seen for five months," Streeter said, noting that the first quarter's growth beats expectations of a 4-percent uplift.
Retail sales of consumer goods, for example, went up 5.8 percent year on year in the first quarter, reversing a decline of 2.7 percent in the last quarter of 2022, according to Tuesday's data. The value-added industrial output increased by 3 percent year on year in the first three months, with a 3.9-percent accelerated expansion in March.
The faster-than-expected growth in the first quarter is just "warming up," Ljubo Jurcic, a prominent Croatian economist and former economy minister, told Xinhua in a recent interview. "This is a good signal of even higher growth in the future."
The Croatian economist's view is echoed by many, including Louise Loo, China lead economist at British think tank Oxford Economics.
"The combination of a steady uptick in consumer confidence as well as the still-incomplete release of pent-up demand suggests to us that the consumer-led recovery still has room to run," Loo said.
"The very healthy print at this early stage will provide the space for authorities to rely on organic growth and for a very gradual policy normalization this year," Loo added.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) last week projected a 5.2 percent growth for China in 2023, up from 3 percent last year. The World Bank, meanwhile, expects China's GDP growth to rebound to 5.1 percent in 2023. Both are in line with China's official growth target of around 5 percent.
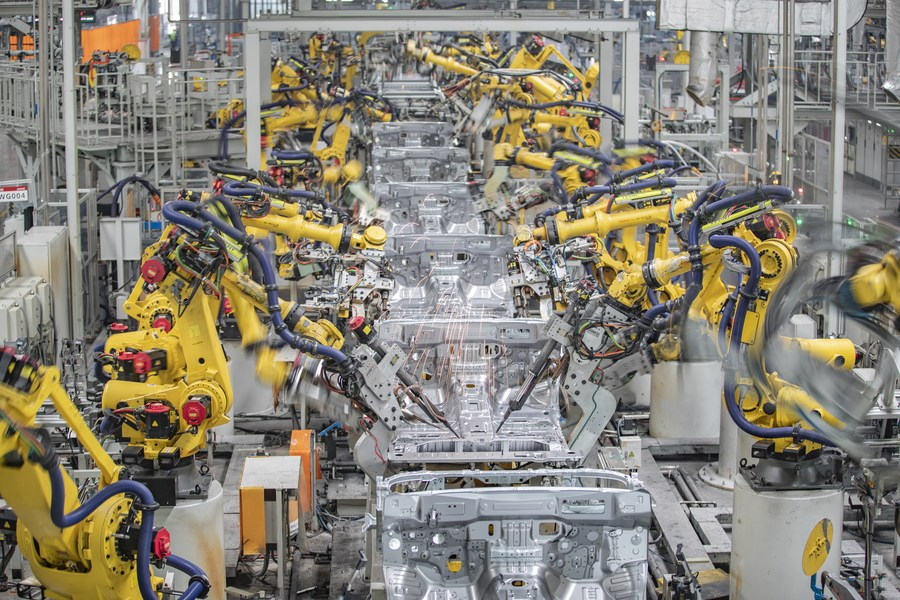

This photo taken on March 1, 2023 shows an intelligent production base of the Great Wall Motors (GWM) in Yongchuan District of Chongqing, southwest China. [Xinhua/Huang Wei]
BRIGHT SPOT OF GLOBAL ECONOMY
With its vast economic volume and deep integration into the global economy, China's stronger-than-expected rebound is widely expected to promote growth in the Asian region and beyond, boosting confidence in global economic recovery.
Against the backdrop of slowing growth of other major economies, China's outstanding economic performance will help promote regional economic development in this context, World Bank East Asia and Pacific Chief Economist Aaditya Mattoo told Xinhua in a recent interview.
According to the World Bank's latest East Asia and the Pacific Economic Update report, economic performance across the region -- while robust -- could be held back this year by slowing global growth, elevated commodity prices and tightening financial conditions due to persistent inflation.
The Washington-based multilateral lender expected growth in East Asia and the Pacific region to accelerate to 5.1 percent in 2023 from 3.5 percent in 2022, saying that "the higher growth is mostly due to China."
The positive spillover effects go far beyond.
Piti Disyatat, assistant governor of the Bank of Thailand, believes that the Chinese economy -- bouncing back from the COVID-19 shocks -- is a stabilizer and driving force for the regional and global economies.
"The world economy is going through a high inflation period and a growth slowdown. China has managed to keep inflation quite low while its growth is bouncing back quite rapidly. That's a stabilizing force, beneficial for both the region and global economy," he said.
Given the size of the economy, China -- with its strong rebound -- would be a "key contributor" to global growth in the coming year, IMF Chief Economist Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas said at a press briefing during the IMF and World Bank Spring Meetings last week.
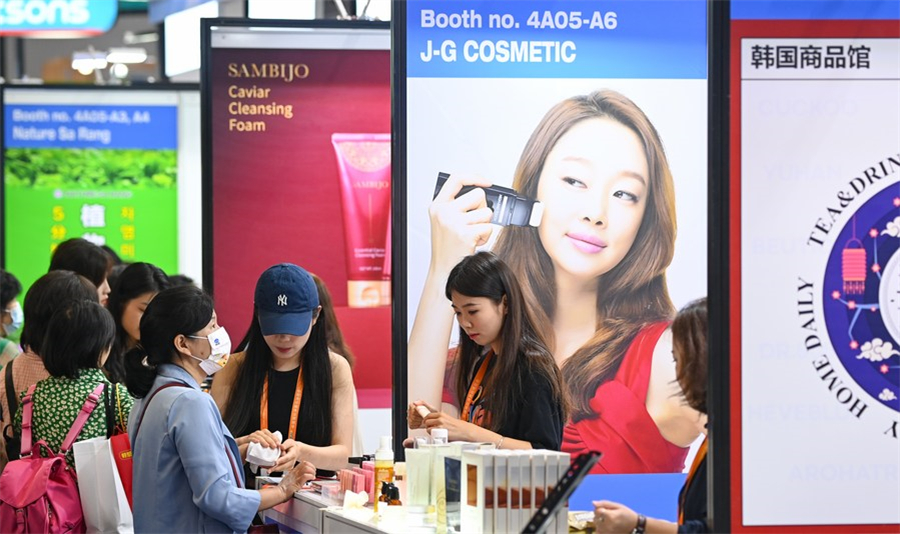

This photo taken on April 12, 2023 shows booths of South Korean enterprises at the third China International Consumer Products Expo (CICPE) in Haikou, south China's Hainan Province. [Xinhua/Yang Guanyu]
The IMF projects global growth to remain around 3 percent over the next five years, the lowest medium-term growth forecast since 1990 and well below the average of 3.8 percent from the past two decades. The multilateral institution also sees economic activity in the United States and the Euro Area slowing, where higher interest rates weigh on demand.
IMF Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva said early this month that as many face a steeper climb, some momentum comes from emerging economies, noting that India and China are expected to account for half of the global growth in 2023.
Asia -- China in particular -- is the bright spot of the world economy, Daniel Leigh, who heads the World Economic Studies division in the IMF's Research Department, told Xinhua in a recent interview, expressing confidence that the Chinese government is in a better position to navigate its economy through international challenges.
"So this is going to provide a boost to a lot of countries," said Leigh. "This is a very positive development" that definitely has positive spillover effects, he said.
For some other developing countries, China's economic growth could benefit them from a long-term perspective.
"The fact that an economy in the size of China is growing at 5 percent to 6 percent is absolutely significant," said Manuel Jose Alves da Rocha, director of the Center for Studies and Scientific Research at the Catholic University of Angola, noting that research on the Chinese economy should focus on the dynamics of development.
"I think that the Chinese experience is rich in lessons, and African countries, particularly Angola, should carefully study the Chinese experience," he said.
Video reporters: Yang Shilong, Pan Lijun, Zhang Mocheng, Wang Feng; Video editors: Jia Xiaotong, Hui Peipei, Yu Jiaming