China's "water tower" sees improving water conservation capacity
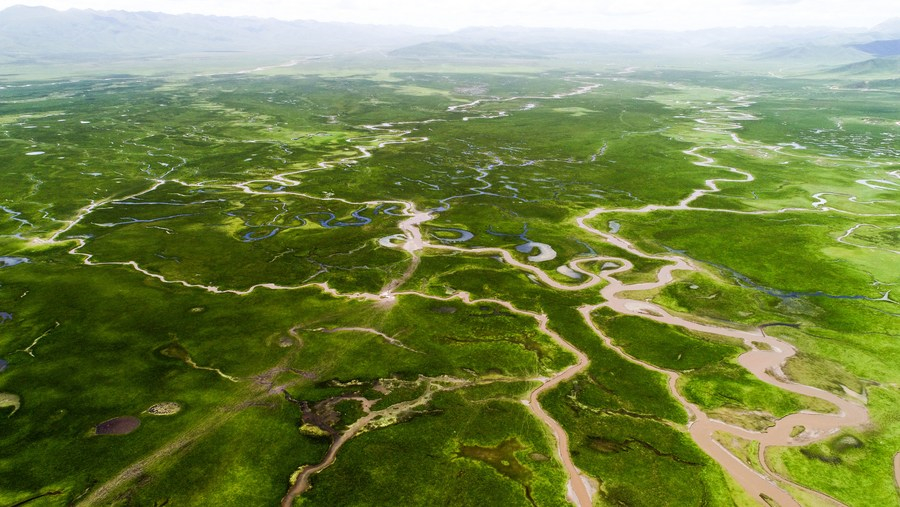

This photo taken on June 28, 2020 shows the Sanjiangyuan National Park in northwest China's Qinghai Province. [Sanjiangyuan National Park Administration/Handout via Xinhua]
XINING -- Northwest China's Qinghai Province has seen an improving water conservation capacity thanks to continued efforts in ecological protection.
Qinghai is home to the Sanjiangyuan area, known as China's "water tower," where the rivers of Yangtze, Yellow, and Lancang originate.
From 2005 to 2021, the average annual volume of outbound water flow from Qinghai was 68.6 billion cubic meters, increasing from the average of 59.6 billion cubic meters between 1956 and 2000.
Qinghai is an arid region with precipitation mainly concentrated in the summer. But water levels at various tributaries in the province tend to be evener throughout the year in recent years, according to Li Qijiang, director of the Qinghai hydrology and water resources monitoring center.
"Such changes prove that the water infiltrating into the soil and aquifer in the basin is increasing, and so is the water conservation capacity in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The improvements demonstrate that a series of ecological protection endeavors China has made in the region are gradually taking effect," Li added.