Resources catapult Ningxia to prosperity
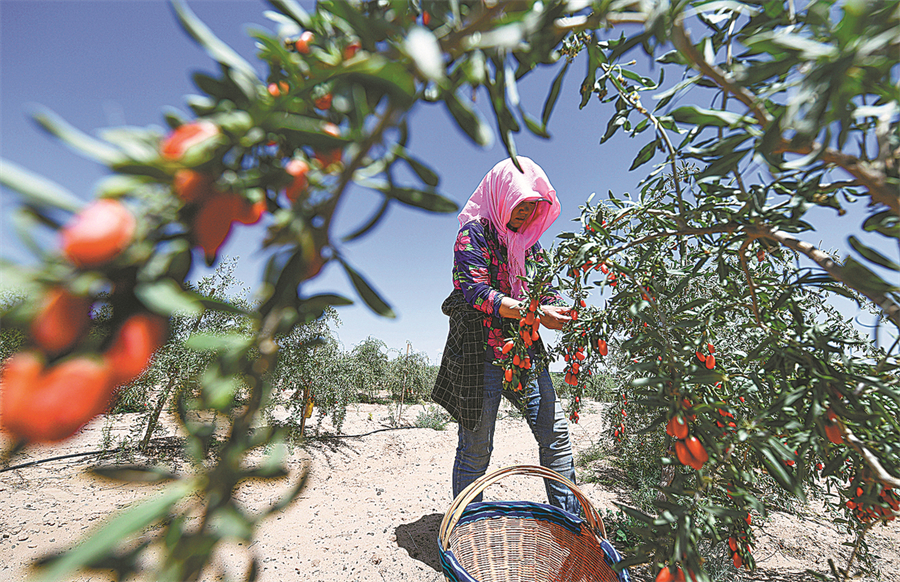

A woman harvests goji berries at a plantation in Wuzhong, Ningxia, in July last year. [Feng Kaihua/Xinhua]
Goji berries, wineries and clean energy propel rapid development in region
Goji berry, also known as wolfberry, has nurtured one of the Ningxia Hui autonomous region's nine pillar industries. Last year, the comprehensive output value of the ubiquitous fruit in the region reached 25 billion yuan ($3.7 billion).
Goji has been a primary ingredient in traditional Chinese, Korean and Japanese medicines for thousands of years, and products derived from the fruit are common worldwide as health foods or alternative medicine remedies.
On the east side of National Highway 110 and about 5 kilometers north of Zhenbeipu West Film City in Yinchuan, Ningxia's capital city, a goji berry town is set to open to the public later this year.
Started in 2010, the plantation has blossomed into a modern farm, incorporating water-saving drip irrigation technology instead of relying on traditional flood methods. Drones have also been introduced to protect the berries from disease and pests.
"It's not only a goji plantation, but also a place where people can pick and eat the berries. It's a place all about goji culture," said Hao Xiangfeng, a national model worker and chairman of Ningxia Berylgoji, which is in charge of developing the town.
When it reaches full operation, the town is projected to generate an output value of 70 million yuan in two years and create more jobs for its residents.
Ningxia's goji berries account for 55 percent of China's total output. By 2025, the total goji plantation area in the region is expected to reach about 46,000 hectares, the output of the fruit will reach 700,000 metric tons and the comprehensive output value will eclipse 50 billion yuan.
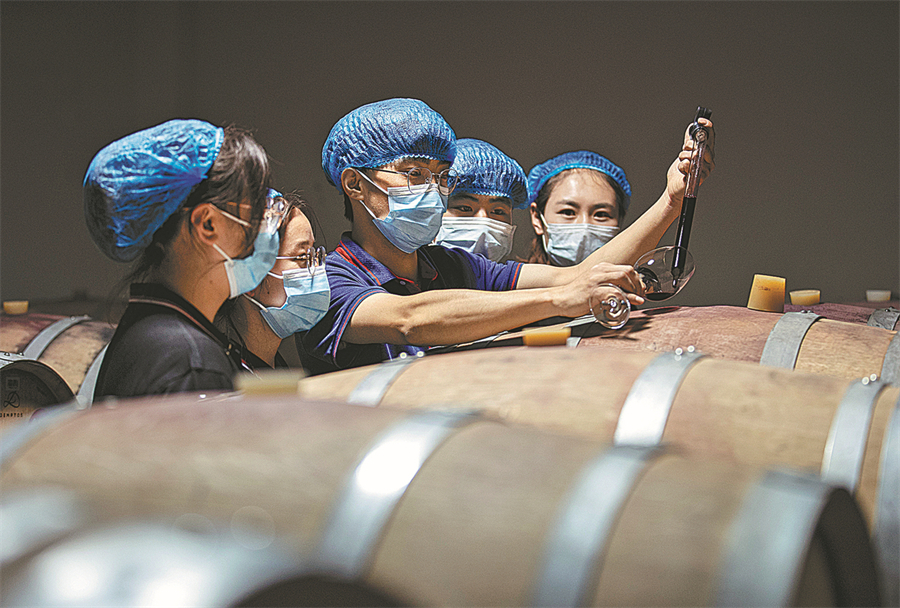
A winemaker (middle) demonstrates how to draw a sample from an oak barrel to students from Ningxia University at a winery in Yinchuan, Ningxia Hui autonomous region, in July last year. [Yang Zhisen/Xinhua]
Meanwhile, Ningxia's wine industry has also grown rapidly in the past decade.
Its first winery was constructed in 1984, and today the region has more than 200 that produce around 130 million bottles a year for an industry valued at 26.1 billion yuan.
In June last year, China set up its first comprehensive experimental zone for the development and opening up of the wine and grape industries in Ningxia, aimed at expanding the region's annual production volume to 300 million bottles and a value of 100 billion yuan by 2025.
The region is also integrating boutique tourism with the wine industry.
The Dulaan Winery Town is a key construction project in the development of the grape and wine industry, with a planned area of 220.2 hectares and a total investment of 2.5 billion yuan.
It is set to boost the integrated development of grape planting, wine brewing and wine tourism, said Zheng Zifeng, CEO of the Ningxia Dulaan Winery.
With its unique resources and geographical advantages, Ningxia has developed more quickly than any other provincial-level region in China over the past decade, with an average annual GDP growth of 7.1 percent, half a percentage point higher than the national level.

The upper reaches of the Yellow River runs through Ningxia. [China Daily]
Liang Yanshun, Party secretary of the region, said the area's GDP exceeded 200 billion yuan in 2011, 300 billion yuan in 2016 and 400 billion yuan last year, with its per capita GDP nearly doubling.
"The past decade has also witnessed the nation's fastest development in terms of both quality and quantity in Ningxia, as well as the biggest changes in the region's urban and rural areas," Liang said.
Clean energy has also greatly expanded since the region became China's first comprehensive demonstration area of new energy in 2012.
Zhang Yupu, chairman of Ningxia, said the installed capacity of wind power and other new energy sources has reached 28.4 million kilowatts, ranking third in China.
This is in line with China's greening plans. The nation is aiming to reach its carbon dioxide emissions peak before 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality before 2060.

Cranes roost at a wetland in Ningxia. [China Daily]
According to officials, the generation capacity for wind and solar power in Ningxia will exceed 50 million kilowatts by 2025, accounting for more than 55 percent of the region's installed capacity.
As a main battleground for poverty alleviation, Ningxia has achieved success in improving the quality of life for its residents. The region's Xihaigu prefecture, one of the poorest areas in China that was labeled the "most unfit place for human settlement" by the United Nations in the 1970s, has eradicated extreme poverty.
In addition, Liang said all of Ningxia's nine counties, with a population of 803,000 rural residents, have been lifted out of poverty, and the region has achieved a balance between high-speed development and environmental protection.
During his visit to Ningxia in June 2020, President Xi Jinping said that efforts were needed to continue building Ningxia into a place featuring economic prosperity, ethnic unity, a pristine environment and wealthier residents.
As a region in the upper arm of the Yellow River, Ningxia has implemented strict measures on ecological and environmental protection to guarantee the water quality of downstream regions.
The region's forest coverage has increased from 11.9 percent to 16.9 percent over the past decade, and its cities have maintained good air quality more than 80 percent of the time for six consecutive years.