China is where I wanted to stay forever — The paper tiger lady's six visits to China

Zhou Enlai and Anna Louise Strong in Chongqing
On her way back to the United States, Strong learned via radio that the South Anhui Incident had taken place. In early February 1942, she received an anonymous air letter from Manila saying that the time had come for her to publish what she knew. Attached to the letter were the full text of the CPC's official order to re-organize the New Fourth Army and the official statement of the spokesperson of the Revolutionary Military Commission. The statement listed a 15-point conspiracy plan by pro-Japanese elements in Chongqing aiming to include China in the Nazi-fascist Axis.
Strong quickly sent the materials to the North American Press Alliance for publication, and wrote a commentary upon request. At that time, many American news agencies and newspapers would choose not to publish anything in favor of the CPC, even if that meant missing an exclusive scoop.
Yet Strong was not someone who would give up easily. She fulfilled her mission despite the difficulties. With the help of friends, she got the information published in the New York Herald Tribune, giving a detailed account of what led to the conflicts in southern Anhui and between the CPC and the KMT, and who was the real troublemaker. The compelling evidence provided by Strong sent shock waves among the Americans, political leaders and the general public alike. It busted the lies fabricated by the KMT and revealed the truth as it was, winning public support for the CPC from around the world.
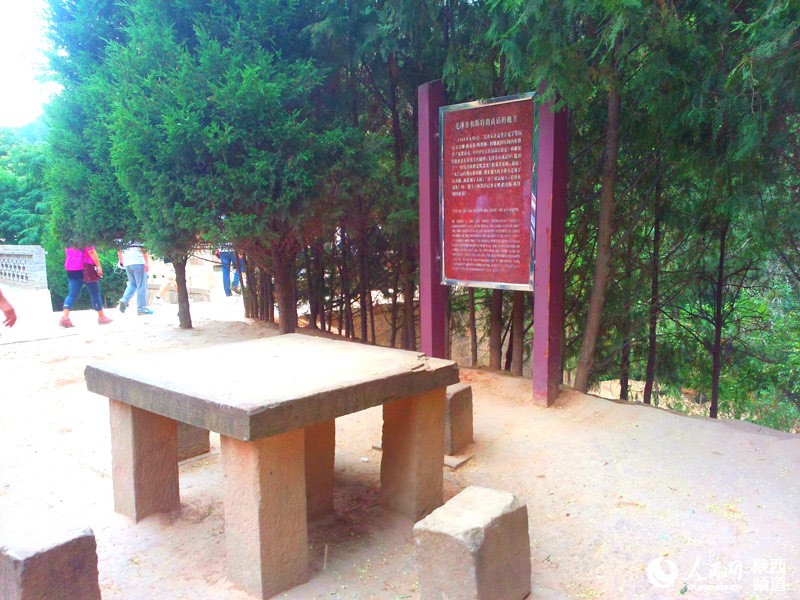

Yangjialing Revolutionary Site in Yan'an, where Mao Zedong talked with Anna Louise Strong in 1946
After China won the War of Resistance against Japanese Aggression, Strong paid her fifth visit to China in June 1946. By a stone table in Yangjialing, Yan'an, She met Mao Zedong. They talked about the developments in the civil war and about the United States, which supported Chiang Kai-shek. Strong asked a difficult question, "Suppose the United States uses the atom bomb?" Mao paused for a moment before he replied firmly, "The atom bomb is a paper tiger which the US reactionaries use to scare people. It looks terrible, but in fact it isn't." Failing to find an English equivalent for paper tiger, the interpreter translated it as scarecrow, following a similar analogy Lenin had made. Strong did not get it. George Hatem,the well-respected doctor known to the Chinese as Ma Haide, was also present. "No, it's not scarecrow," he said. "Should be paper tiger." Mao liked this translation. "A paper tiger is not something dead to scare crows. It scares children. It looks like a terrible tiger but actually, being made of pressed paper, it softens when damp and is washed away in a heavy rain," he explained. "All reactionaries are paper tigers. In appearance, the reactionaries are terrifying, but in reality, they are not so powerful. From a long-term point of view, it is not the reactionaries but the people who are powerful."
Strong later compiled an English transcript of this conversation. The Publicity Department of the CPC Central Committee translated it into Chinese for Party members and cadres in the Yan'an border region and the liberated areas to study and discuss. In April 1947, Strong published the English transcript in the New York-based monthly journal Amerasia under a revised title "A World's Eye View from a Yenan Cave: An Interview With Mao Tze-tung", which became the official English version of her conversation with Mao. It was soon translated and published by a number of Chinese-language publications in the KMT-controlled areas and Hong Kong. Thus, records of the conversation spread around quickly with a far-reaching impact.