Developing a Uniquely Chinese System of Intellectual Property
On November 30, 2020, the Political Bureau of the 19th CPC Central Committee held a collective study session on strengthening protection of intellectual property (IP). President Xi Jinping chaired the session and gave an important speech in which he affirmed China's historic achievements in, and elaborated on the great significance of, IP protection, discussed the current situation and tasks facing such work, and the Party's main policies aimed at strengthening IP protection.
I. Historic achievements in developing a uniquely Chinese system of IP
Looking back at the development path of IPR in China, we have accomplished in mere decades what took developed countries centuries to achieve. We have taken a historic leap, creating something out of nothing and scaling up at great speed, becoming an IP power in the process. Our achievements are enormous, and it is worth recapping our experience.
The CPC's leadership over IPR has consistently grown stronger.
Soon after the founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949, China began looking at how to protect IP, though it was not until the Third Plenary Session of the 11th CPC Central Committee in 1978 that formal processes began to be put in place. In 2008, the Outline of the National Intellectual Property Strategy was implemented, and IP protection was elevated to the status of a national strategy. At the 18th CPC National Congress in 2012, the Central Committee gave even greater prominence to IP work, and President Xi subsequently issued a series of instructions and presided over multiple meetings of the Central Commission for Comprehensively Deepening Reforms (formerly the Central Leading Group for Comprehensively Deepening Reforms), which approved documents including the Decisions on Strengthening the Protection of Intellectual Property and the Overall Pilot Reform Program for Comprehensive Management of Intellectual Property Rights and issued important directives. The CPC Central Committee and the State Council also issued the Action Plan for the In-depth Implementation of the National Intellectual Property Strategy (2014-2020), Several Decisions of the State Council on Accelerating the Construction of a Powerful Intellectual Property Nation under New Conditions, and National Intellectual Property Protection and Application in the 13th Five-Year Plan, and established institutional mechanisms including an inter-ministerial joint committee for the implementation of the State Council's IP strategy. Moreover, the establishment of the State Administration for Market Regulation and the reorganization of the China National Intellectual Property Administration have created centralized and unified management over patents, trademarks, geographical indications of origin, integrated circuit layout designs, and the comprehensive enforcement of patents and trademarks, greatly enhancing administrative management. Meanwhile, judicial protection of IP has been significantly enhanced, with the establishment of multiple IP courts including that of the Supreme People's Court.
China's IP legal system is improving.
Since the 1980s, China has formulated and promulgated a whole raft of IP laws and regulations, such as the Trademark Law, Patent Law, Copyright Law, Law Against Unfair Competition, Regulations on the Protection of New Plant Varieties, Regulations on the Protection of Integrated Circuit Layout Design, and Regulations on the Protection of Olympic Symbols. China is establishing a comprehensive IP legal system that complies with internationally accepted rules and is constantly revising and improving it based on practical experience. China's newly formulated Civil Code, in particular, has established important legal principles for IP protection, while revisions to China's Patent Law, Trademark Law, and Copyright Law have established punitive compensation for infringements that are at the high end of the international scale, providing strong legal guarantees for stringent IP protection. In addition, China has become a party to almost every major international IP treaty, enthusiastically fulfilled its responsibilities and obligations under international pacts, and is an increasingly staunch defender, important participant, and proactive developer of international IP regulations.
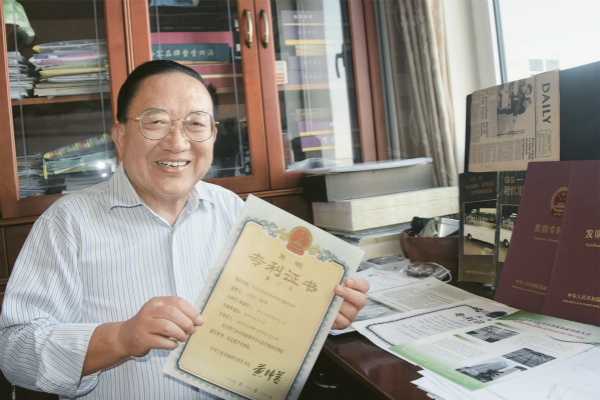

Hu Guohua displays the patent certificate he was granted more than three decades ago. On April 1, 1985, the first day that the Patent Law of the People's Republic of China came into force, Mr. Hu, who was then employed as an engineer at the Ministry of Aerospace Industry, submitted China's first patent application, No. 85100001.0. From then on, patent work in China moved onto the right track and started making rapid advances. PHOTO BY CNS REPORTER SUN ZIFA

The State Council Information Office holds a press conference in Beijing regarding the 2019 report on the latest developments in China's intellectual property protection efforts and business environment, April 26, 2020. PHOTO BY CNS REPORTER YANG KEJIA
IP protection in China has become stronger.
In the past several decades, IP rights in China have grown out of nothing and been continuously strengthened. Since the 18th CPC National Congress, in particular, IP protection has become stronger, with a proliferation of core patents, well-known trademarks, premium copyrights, and high-quality geographical indication (GI) products. In 2020, there were 1.58 invention patents per 1,000 people in China (excluding Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan), and valid trademark registrations reached 30.2 million, more than four-fold higher than that in 2012. In 2019, China ranked first in the world for the number of PCT international patent applications, and third in the world for international trademark applications through the Madrid system. Public satisfaction with IP protection in China increased from 63.69 points in 2012 to 80.05 points in 2020. China's ranking in the Global Innovation Index moved up from 34th in 2012 to 14th in 2020, placing it first among middle-income economies and making it one of the fastest-improving countries in the world. Of the world's 5,000 leading brands, China accounts for 408, with a combined value of US$1.6 trillion. China's position in the World Bank's Ease of Doing Business ranking jumped from 91st in 2012 to 31st in 2020, and it has been among the top ten economies with the largest improvement in their business environments for two consecutive years. In 2019, the value added of patent-intensive industries accounted for 11.6% of China's GDP. The latest data show that the direct output value of enterprises using special geographical indications is RMB639.8 billion yuan. IP protection in China has rapidly become stronger, lending solid support to national economic and social development.
International cooperation on IP is continuously expanding.
China is promoting IP cooperation at the multilateral, peripheral, mini multilateral, and bilateral levels, creating a new form of international cooperation on IP. China is deeply involved in multilateral initiatives under the framework of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in order to resolutely safeguard the multilateral intellectual property system, and consented to establishing a WIPO Office in China. WIPO was also behind the first international treaty on intellectual property rights to be signed in China and named after a Chinese city: the Beijing Treaty on Audiovisual Performances. China has organized two high-level conferences on IP and the Belt and Road Initiative and achieved important results through eight practical cooperation projects, including cooperation on IP protection, business reviews, basic capacity building, and public awareness. China is promoting in-depth and pragmatic cooperation on IP with the United States, Europe, Japan and South Korea, with other BRICS countries, ASEAN, and Africa, and helped to set up the Patent Prosecution Highway (PPH) program together with 30 countries and regions. Following 22 rounds of negotiations, the China-EU Geographical Indications Agreement was signed, covering a total of 275 GI products of both parties, which has boosted economic and trade relations between China and the EU. As a result, China's influence and circle of friends in the field of IP is growing.
The thinking and approaches behind IP work are continuously improving.
China seeks progress amid stability and is focused on promoting high-quality development, particularly high-quality economic and social development supported by high-quality development of IP rights. China has adopted a systematic approach and is focusing on protecting IP by coordinating strict, widespread, rapid, and coordinated protection of IP rights; focusing on IP applications by coordinating the construction of mechanisms and platforms and promoting industry; and focusing on the management of IP rights by creating a complete chain, from invention, to application, protection, management and services, that runs through all types of IP, bringing comprehensive benefits. China recognizes the importance of having solid foundations, so it is continuing to improve the quality and efficiency of investigations, strengthening local IP protection, and carrying out extensive IP publicity to improve the public's awareness of IP issues.
II. Major issues affecting contemporary IP protection
It is vital to understand the importance of IP protection.
IP protection has a bearing on the modernization of our national governance system and governance capacity, on achieving high-quality development, on the wellbeing of the people, on the wider context of opening up, and on national security. Given the importance of IP protection, China must assimilate efforts with its overall economic and social development and strongly support it in all respects. In particular, it is necessary to improve modern IP systems and continue reforms to promote market-based allocations of factors of production through stringent IP protection, so that the market can play the decisive role in allocating resources while the government can play its role better. It is also necessary to crack down on all types of infringement and counterfeiting in accordance with the law to improve the quality of the supply system and promote high-quality development. China needs to safeguard the rights and interests of consumers so that people can consume with confidence; to optimize the business environment by creating a new, more open economy and strongly supporting all aspects of opening up; to protect key and core technologies independently researched and developed in China; and to implement a review system for transferring IP rights.
It is vital to grasp the strategic aspect of IP protection.
President Xi pointed out that to build a modern socialist country in all respects, China must incorporate it into its national strategies and consider the requirements posed by the new development stage, comprehensively strengthen IP protection, construct a modern economic system, encourage innovation throughout society, and develop a new development dynamic. President Xi's instructions have provided insight into the goals and tasks of IP protection in the new era. China needs to further enhance its sense of responsibility, of mission, and of urgency regarding IP protection in the new era, understand the role of IP in building a modern economic system, and strengthen IP protection to encourage internal innovation and greater openness to the outside world. We need to promote a market system predicated on high standards, develop a more open economy, and support the construction of a new development dynamic with the domestic economy and international engagement providing mutual reinforcement, and the former as the mainstay.
It is vital to recognize the historical significance of IP protection.
President Xi has indicated that China is making the transition from a major importer of IP to a major creator of IP, and IP work is changing from being about pursuing quantity to improving quality. In his speech, President Xi has affirmed the achievements that have been made in IP work, emphasized the historical significance of this work, and encouraged further efforts in this regard. China must use its historical achievements in the development of IP to increase the enthusiasm of officials and ordinary workers toward entrepreneurship. It must understand the new circumstances, features, and tasks of developing IP rights, and continue to boost a uniquely Chinese system of IP. In particular, China needs to highlight the theme of the times, which is high-quality development; put in place even higher standards for the creation, use, protection, and management of IP rights as well as IP services; redouble its efforts in international cooperation on IP protection; and seek progress in IP protection amidst stability and high-quality development of IP from a higher starting point.
It is vital to understand the fundamental stance of IP protection.
The people's stance is the fundamental political stance of the CPC. President Xi has pointed out the need to uphold the principles of acting in our own best interests, prioritizing the people's interests, and providing fair and reasonable protection. China must not only stringently protect IP rights but also prevent the excessive expansion of individual and corporate rights, to both protect public interests and encourage innovation. In his speech, President Xi reflected this people-centered development concept and clearly expressed these values. The fundamental criterion for assessing the effectiveness of IP protection efforts should be whether people's legitimate IP rights and interests are protected, whether innovation is stimulated, and whether economic and social development is promoted. To adhere to the principle of acting in its own best interests, China must absorb and learn from others' achievements in IP system development around the world and then build its own system suited to its national conditions and development requirements.

Officials from national and local government departments in charge of intellectual property matters offer consultation services on IP protection at the 2020 China International Fair for Trade in Services, helping to ensure a successful event. PHOTO BY CHINA INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY NEWS REPORTER JIANG WENJIE
To provide fair and reasonable IP protection, China must balance the interests of rights holders with those of the general public. We must protect the legitimate rights and interests of rights holders but also promote the dissemination and utilization of knowledge, to ensure the benefits of innovation enrich the lives of ordinary people.
It is vital to comprehend the strategies involved in international IP cooperation and competition.
President Xi said in his speech that we must promote the concept of a global community with a shared future, adhere to the principles of openness, inclusiveness, and balance, participate meaningfully in global IP governance under the WIPO, promote improvements to rules and standards covering IP and related international trade and investment, and develop a more just and rational global IP governance system. China needs to deepen IP cooperation with countries along the Belt and Road and encourage knowledge sharing. President Xi also clarified the strategic necessity of international IP cooperation and competition and said that China needs to focus on its national reform and opening up while strengthening international IP cooperation. He particularly noted the need to engage with the WIPO, the Belt and Road countries, BRICS, as well as the US, Europe, Japan, and South Korea to promote improvements to international governance of IP rights. China also needs to balance domestic and overseas IP protection to both safeguard the legal IP rights of foreign-funded enterprises in China in accordance with the law and ensure foreign governments strengthen their protection of Chinese IP rights.
It is vital to know the key work involved in IP protection.
In his speech, President Xi set out important measures for strengthening the top-level design of IP protection, enshrining IP protection in law, strengthening protection across the entire IP chain, further reforming China's IP protection system and mechanisms, coordinating international IP cooperation and competition, and safeguarding national security in the area of IP. These are highly targeted and instructive measures aimed at protecting IP based on the bigger picture and with an eye to the future. These six aspects are interrelated and integrated, and they constitute the key areas and core links of IP protection.
III. Reform and development of IP
China must have a forward-looking approach in making top-level design of IP protection.
China should have a strategy for becoming a country strong on IP and formulate a national IP protection and utilization plan for the 14th Five-Year Plan period with clear goals, tasks and measures, implementation blueprints, and annual plans, to ensure orderly implementation. China must balance the interests of rights holders with those of the public by strictly protecting IP while preventing the excessive expansion of rights. Patent quality improvement projects are needed to alleviate bottlenecks, and industrial infrastructure should be rebuilt to encourage the creation and storage of relevant IP. China needs to continue with its trademark and brand strategies, initiate the implementation of geographical indications to assist rural revitalization, and support high-quality economic and social development.
China must keep abreast of the times and better enshrine IP work in law.
We must strictly implement IP regulations contained in the Civil Code, revise the Rules for the Implementation of the Patent Law of the People's Republic of China, establish a national working mechanism for handling patent infringement disputes, and put in place an early settlement mechanism for drug patent disputes. We need to investigate and present the case for revising the Trademark Law and strengthen legislation on geographical indications. China must strengthen its guidance system for administrative enforcement of IP and unify its authorization, administrative enforcement, and judicial decision standards. We must promote links between IP departments and courts to facilitate online litigation and encourage diverse solutions to IP disputes. The government must work with relevant departments to bolster law enforcement and thoroughly rectify key fields and regions where infringement and counterfeiting are rife.
China needs to make concerted efforts to strengthen protection along the entire IP chain.
It is necessary to strengthen coordination between departments to improve IP protection at every link in the chain, from review and authorization, to administrative law enforcement, judicial protection, arbitration and mediation, industry self-regulation, and public credibility. China needs to improve its IP rights management system to enhance its protection capabilities. We should create a convenient IP public service system by implementing projects to upgrade capabilities and promote standardization. It is necessary to strengthen the development of IT-based and intelligent IP infrastructure for integrated development of online and offline IP protection. China should advance its pilot project on credit-based hierarchical and classified supervision and introduce an IP integrity system. We also need to strengthen publicity, education, and public welfare training to enhance public respect for and protection of IP rights.
China must continue to innovate and further reform its IP protection system and mechanisms.
We must continue to implement reforms on IP protection initiated by the CPC Central Committee since the 18th CPC National Congress to ensure their efficacy. China needs IP policies tailored to specific industries and regions, and it should improve its IP review system, refresh review concepts, technology and practices, and continue to improve the quality and efficiency of reviews, to better meet the needs of the people. We must improve IP protection in new fields, such as big data, AI, and gene technology, to facilitate their development. We need to improve our IP evaluation system, value evaluation mechanism and standards, and IP ownership system, as well as create related systems to prevent IP abuses and allow the realization of IP's economic value.
China must be proactive in international IP cooperation and competition.
We should participate in the multilateral governance of the WIPO, work harder toward our accession to the Hague Agreement Concerning the International Registration of Industrial Designs, and actively participate in negotiations on provisions concerning IP in relevant free-trade agreements, so as to help improve international rules and standards on IP and relevant international trade and investment as well as to make the global IP governance system more just and rational. We must broaden channels to make the message about IP protection in China heard and establish a good international image of China as a protector of IP in accordance with the law. China should also deepen IP cooperation and innovation with countries along the Belt and Road and fully implement provisions on IP contained in the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership agreement and the China-EU agreement on cooperation on, and protection of, geographical indications to promote trade.
Shen Changyu is Commissioner of the China National Intellectual Property Administration.
(Originally appeared in Qiushi Journal, Chinese edition, No. 3, 2021)